Magnesium Glycinate
Share
Magnesium Glycinate: Unlocking the Potential for Wellness and Better Sleep
Magnesium is an essential mineral involved in over 300 biochemical processes in the human body, including energy production, muscle relaxation, and sleep regulation. Magnesium glycinate, a chelated form of magnesium combined with the amino acid glycine, stands out for its high bioavailability and calming effects, making it an excellent choice for improving overall wellness and sleep quality. This article explores its importance, deficiency symptoms, and benefits, based on current research.
Why Magnesium is Essential for Health
Magnesium is vital for muscle and nerve function, regulating blood pressure, and supporting bone health. Despite its critical role, magnesium deficiency is common, partly due to decreased magnesium content in modern diets as a result of soil depletion and food processing.
Magnesium Deficiency: Causes and Symptoms
Many individuals consume less magnesium than the recommended daily allowance (RDA). The U.S. Department of Agriculture reports that nearly 48% of Americans do not meet magnesium intake recommendations. This can lead to various health issues.
Common Symptoms of Magnesium Deficiency
| System | Signs of Deficiency |
|---|---|
| Neurological | Anxiety, irritability, poor concentration |
| Muscular | Muscle cramps, spasms, and tension |
| Cardiovascular | Irregular heartbeat, high blood pressure |
| Sleep | Difficulty falling asleep, frequent wake-ups |
The Benefits of Magnesium Glycinate
Magnesium glycinate offers several advantages over other forms of magnesium:
- Improved Sleep Quality: Magnesium has been shown to regulate melatonin production and calm the central nervous system, which is critical for restorative sleep.
- Enhanced Absorption: Glycinate form is highly bioavailable, making it gentle on the stomach and ideal for those with gastrointestinal sensitivity.
- Stress Reduction: The glycine component has calming properties, reducing stress and anxiety.
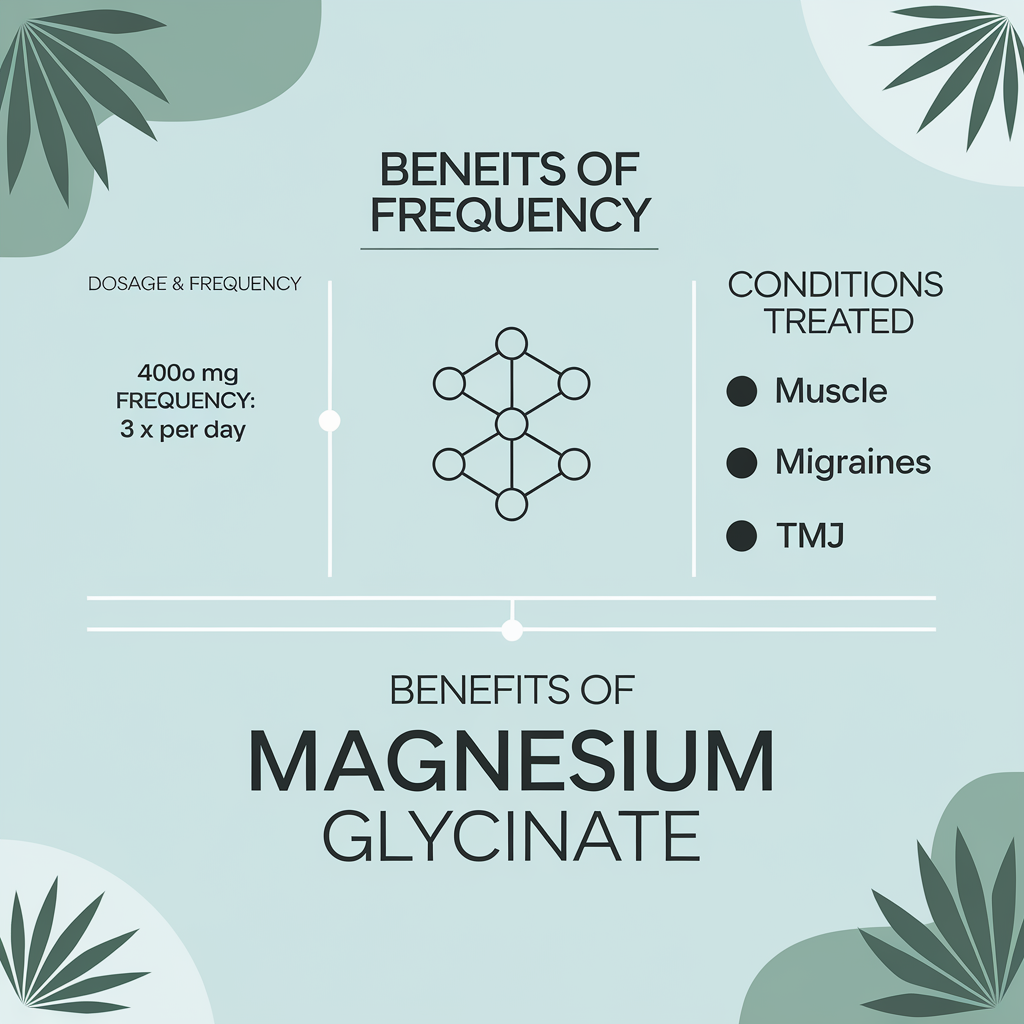
- Muscle tension: reduces muscle tension and tension headaches, can be used during the day when symptoms develop. Espeically relevant for those who get hip and lower back pain whilst driving or shoulder / neck pain when working at the computer for long hours.
Dietary Sources of Magnesium
While supplementation is effective, a diet rich in magnesium can also help. Foods high in magnesium include:
- Pumpkin Seeds (156 mg/oz)
- Spinach (78 mg/½ cup cooked)
- Almonds (80 mg/oz)
- Black Beans (60 mg/½ cup).
Research Highlights on Magnesium Glycinate
Studies have associated magnesium supplementation with improvements in sleep duration and quality. For example, research from the CARDIA study found that higher magnesium intake reduced the likelihood of short sleep duration (<7 hours) and improved overall sleep quality.
Conclusion
Magnesium glycinate is an effective option for those looking to improve their wellness and sleep. Whether consumed through diet or supplementation, it plays a vital role in maintaining optimal health. Consulting a healthcare provider to evaluate individual needs is recommended.
References:
- CARDIA Study, Sleep and Magnesium Intake.
- USDA Magnesium Sources and Deficiency Data.